The atmospheric gases and a greenhouse work in quite different ways, but the resulting effect, higher temperature in both cases, has led to the nomenclature "greenhouse gases" for the atmospheric gases responsible for the atmospheric warming effect Although this nomenclature is misleading, it is in such common use that we use it here as well Greenhouse effect refers to a process where thermal radiation from the earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and then radiated in all directions The main greenhouse gases include Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planet

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
What is a greenhouse effect definition
What is a greenhouse effect definition-When a molecule absorbs an amount of energy and vibrates, it has gone from its ground state to a vibrational excited state Just like the transitions between electronic ground state and electronic excited states, only specific amounts of energy can be absorbed Reciprocal wavelength, 1/λ, is directly proportional to energyTherefore, it results in the greenhouse effect The solar energy is absorbed by the earth's surface and then reflected back to the atmosphere as heat




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences theGreenhouse gas definition is any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect How to use greenhouse gas in a sentenceAnother version of a greenhouse is what happens inside an automobile parked in the sun The sun's light and heat gets into the vehicle and is trapped inside, like the plastic bag around the jar The temperature inside a car can get over 1 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees
Greenhouse gases absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth's surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more detailsThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of lifeThe Chemistry of the Greenhouse Effect Introduction The greenhouse effect remains one of the reasons Earth is habitable to humans and other organisms It relies on mainly on five gases, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and nitrous oxide These gases work together to trap infrared radiation within the Earth's atmosphere in order
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown These structures range in size from small sheds to industrialsized buildings A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frameAct as indirect greenhouse gases through their influence on atmospheric chemistry, eg, formation of tropospheric O 3 or changing the lifetime of CH 4 The emissions of NO x and CO are dominated by human activities The abundance of CO in the Northern Hemisphere is about twice that in the Southern Hemisphere and has increased in the second half of the thGreenhouse effect Some thermal energy from the Earth's surface escapes into space If too much thermal energy escaped, the planet would be very cold However some gases in




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education
Greenhouse effect definition The greenhouse effect is the problem caused by increased quantities of gases such as Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples The term "greenhouse effect" is mentioned a lot when we talk about climate change But what exactly does it mean?The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming How the Greenhouse Effect Works Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an atmospheric constituent that plays several vital roles in the environment It absorbs infrared radiation in the atmosphere It plays a crucial role in the weathering of rocks It is the raw material for photosynthesis and its carbon is




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
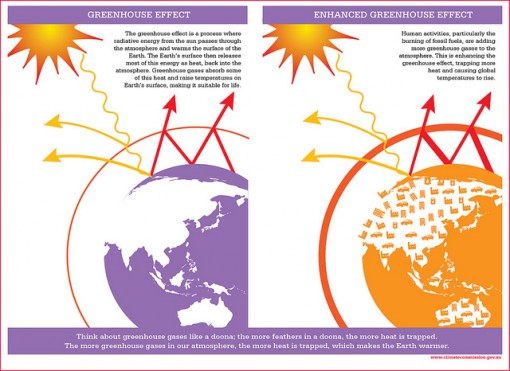



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future
Define greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth Some heat is reflected back through the atmosphere, while some isThe greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring process that aids in heating the Earth's surface and atmosphere It results from the fact that certain atmospheric gases, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane, are able to change the energy balance of the planet by absorbing long wave radiation emitted from the Earth's surface Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to



The Greenhouse Effect




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated CO2 GHG effectiveness is a ln function of CO2 consentration This means that the slope of that ln curve is the effectiveness The problem is that the slope of the ln curve (or the first partial derivative) is equal to 1/ (CO2 consentration) For example, at 0 ppm the slope is 1/0 and at 400 ppm the slope is 1/400Greenhouse effect, causing global warming The two most abundant gases in the atmosphere, nitrogen (comprising 78% of the dry atmosphere) and oxygen (comprising 21%), exert almost no greenhouse effect Instead, the greenhouse effect comes from molecules that are more complex and much less common Water vapour is the most important greenhouse




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
In short it is the natural process that warms the Earth's surface The process is called the greenhouse effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the planet works in a similar way to a greenhouseGreenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases are thought to be the main contributor to climate change (The Greenhouse Effect) They are very efficient in trapping heat into the atmosphere;All gases whose molecules have three or more atoms are greenhouse gases—carbon dioxide (CO 2), water vapor (H 2 O), and methane (CH 4) are important greenhouse gases that have maintained Earth's warm temperature for billions of years Source Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
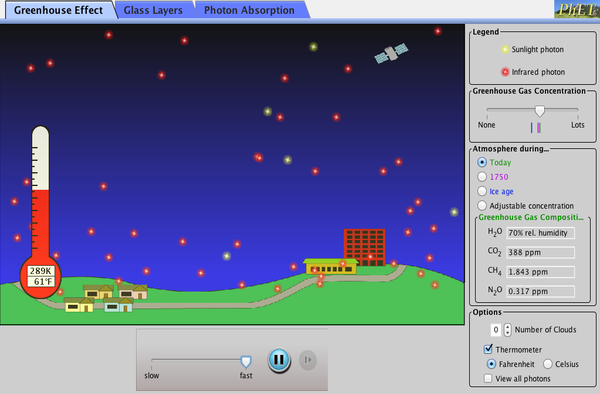



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Heat Phet Interactive Simulations




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxidesHow do greenhouse gases affect the climate?The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases These molecules in our atmosphere are



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
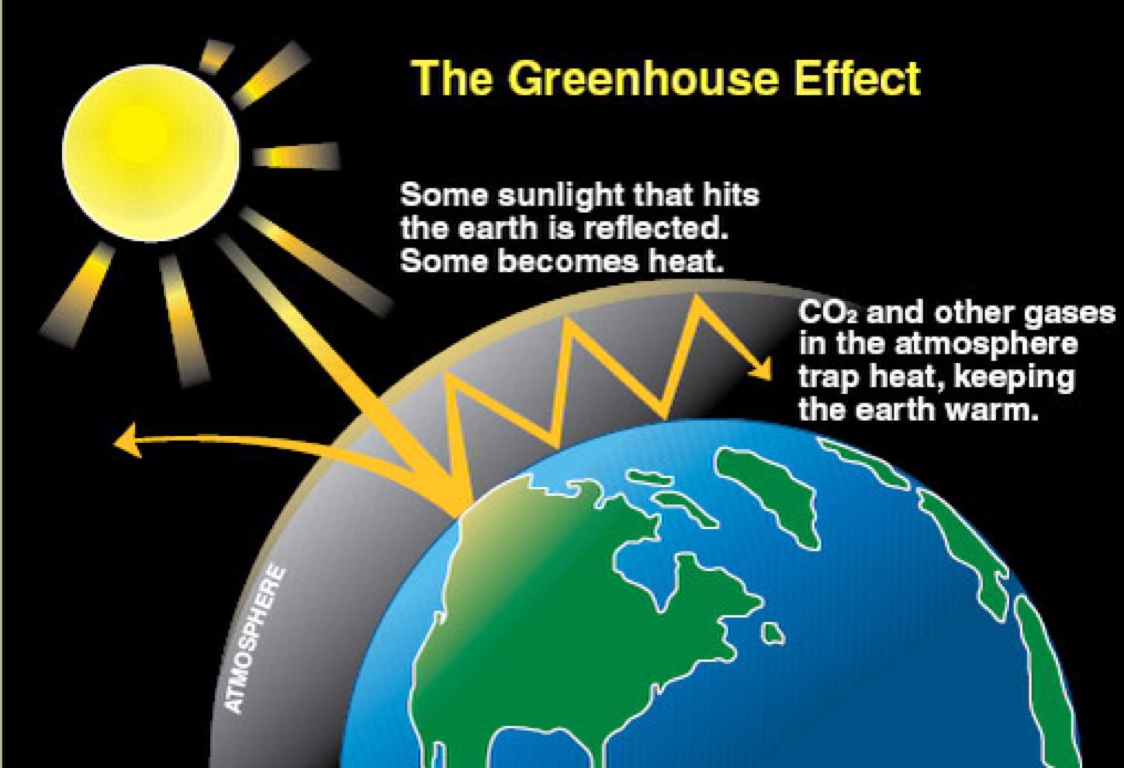



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)To balance this input of solar radiation, the Earth itself emits radiation to space Some of this terrestrial radiation is trapped by greenhouse gases and radiated back to the Earth, resulting in the warming of the surface known as the greenhouse effectThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases



1




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education
The enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forests The natural greenhouse effect The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surfaceWhat could happen if this greenhouse effect changed the Earth's climate?



Carbon Cycle And The Earth S Climate




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gasesThe greenhouse effect meaning 1 an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere (= mixture of Learn moreExplore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds?




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Youtube
The complex, which they designed, promises to open up a new area of carbon chemistry that might allow greenhouse gases to be converted into useful molecules with minimal energy input If fossil fuels burn completely, the end products are carbon dioxide and waterGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



3
One way in which humans have affected the climate is by increasing emissionsof greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases absorb infrared (longwave, heat) radiation This is the form of the sun's energy reflected off the earth's surface Greenhouse gases then radiate heat energy back toward the earthThe greenhouse effect is the process in which the emission of infrared radiation by the atmosphere warms a planet's surface The name comes from an analogy with the warming ofGreenhouse effect A term used to describe the heating of the atmosphere owing to the presence of carbon dioxide and other gas es Without the presence of these gases, heat from the sun would return to space in the form of infrared radiation




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases



The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect
Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



Untitled Document




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay



Global Warming




What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Inside Climate News




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Methane Is Like Co2 On Steroids When It Comes To Trapping Heat




What Is The Greenhouse Effect American Chemical Society




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect World101
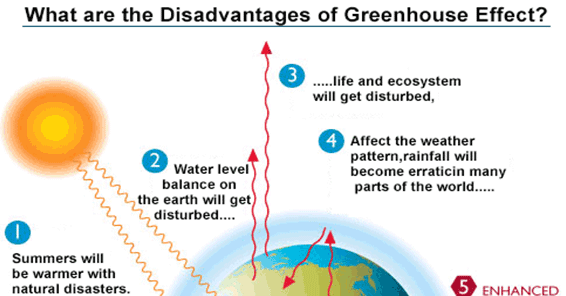



Disadvantages Of Greenhouse Effects Myassignmenthelp Com



Www Extension Purdue Edu Extmedia Id Id 506 W Pdf




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences




The Greenhouse Effect Introduction To Chemistry




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Environmental Chemistry Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ppt Download
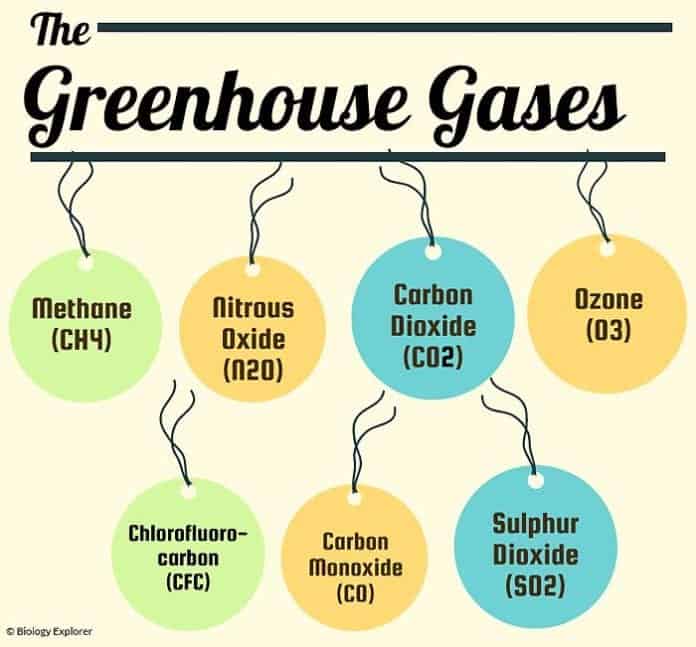



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change



Greenhouse Effect




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



Untitled Document
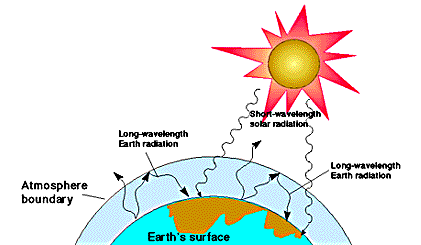



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases
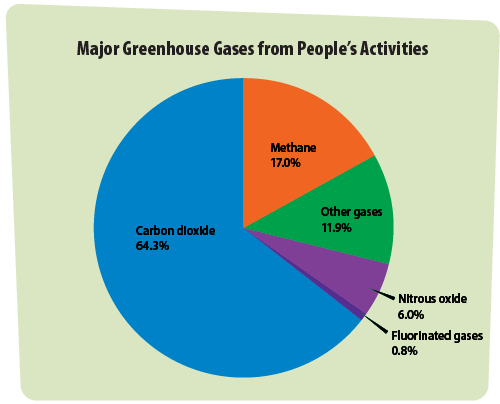



What Is The Relation Between Covalent Bonding And The Greenhouse Effect



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Climate Change Ten Year Retreat




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
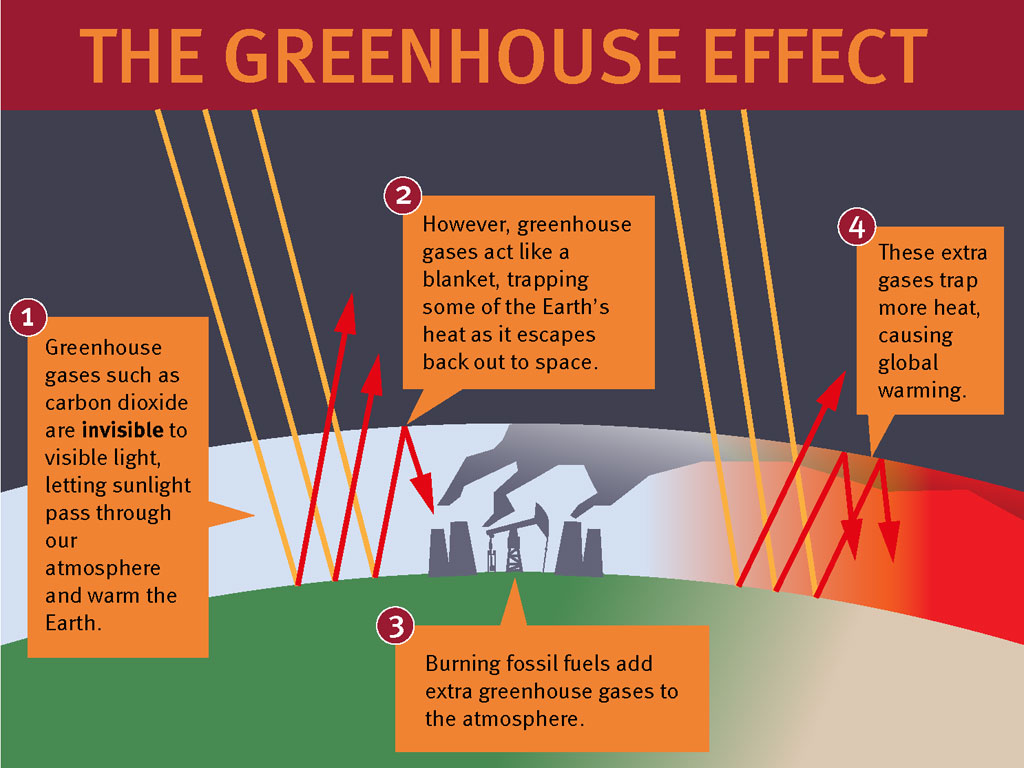



Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
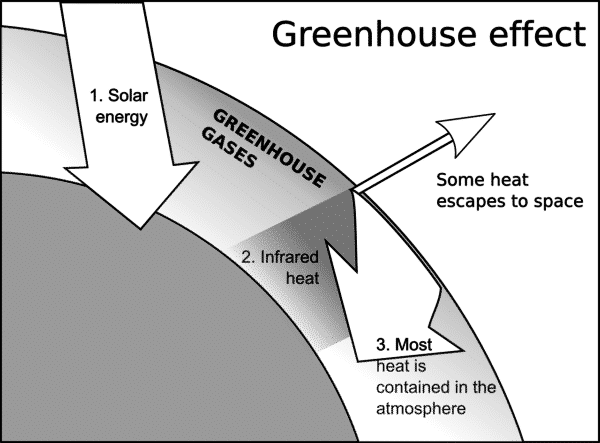



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub



1




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
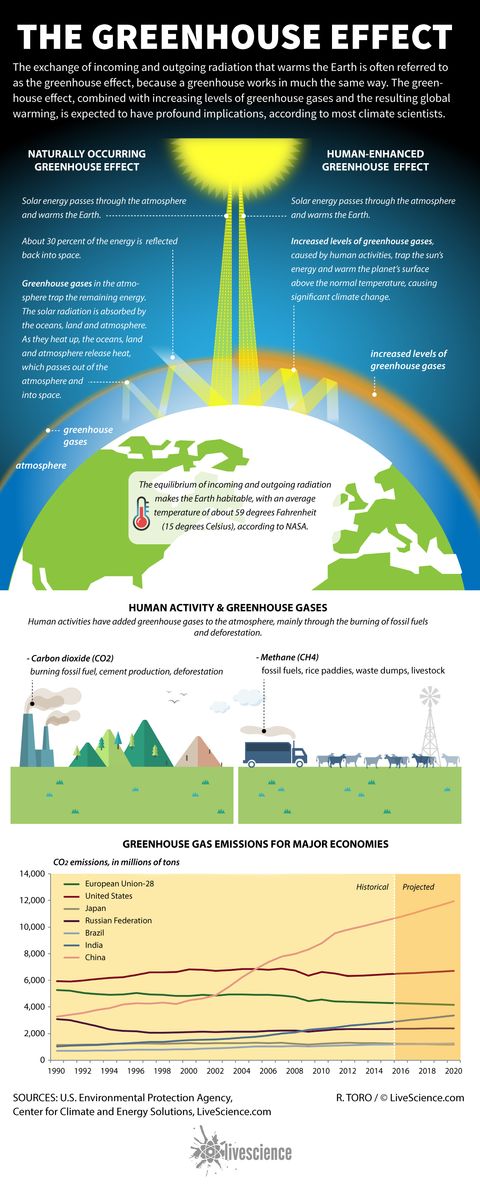



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Sf6 Worries The Most Potent And Persistent Greenhouse Gas Advanced Science News



Greenhouse Effect
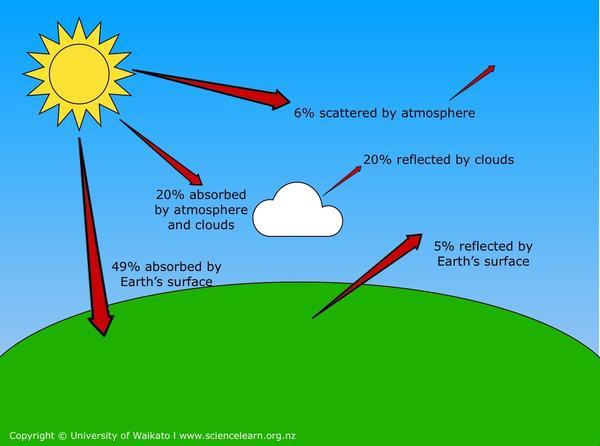



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub



Team Braunschweig Project Content 14 Igem Org




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society
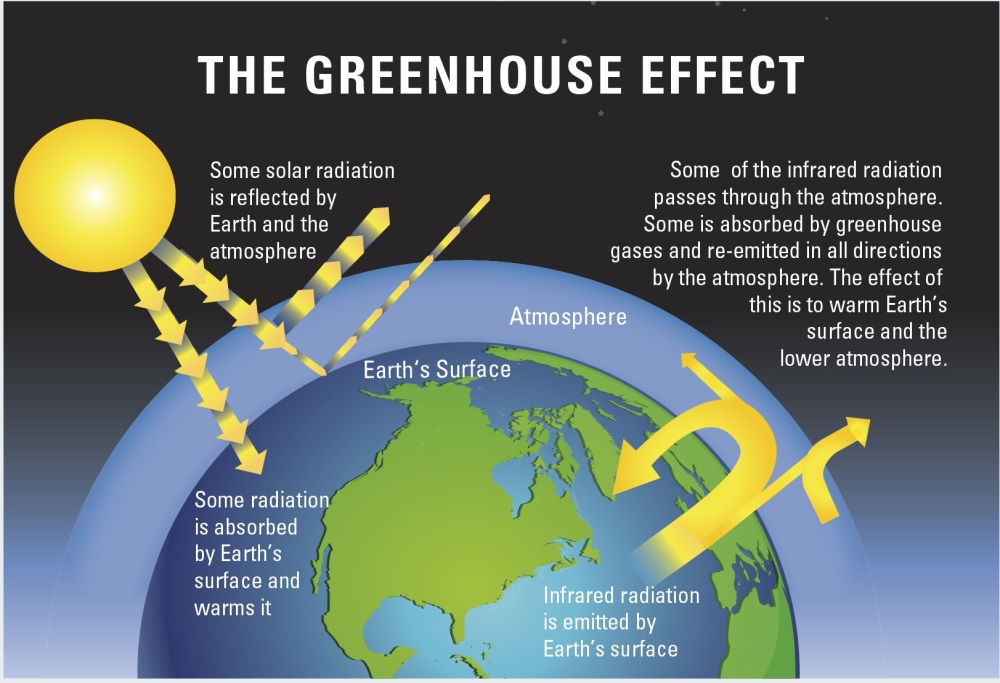



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect E 3 Pages Definitions 2 Description 3 Greenhouse Gases 4 Greenhouse Gases Effect On Atmosphere Ppt Download




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
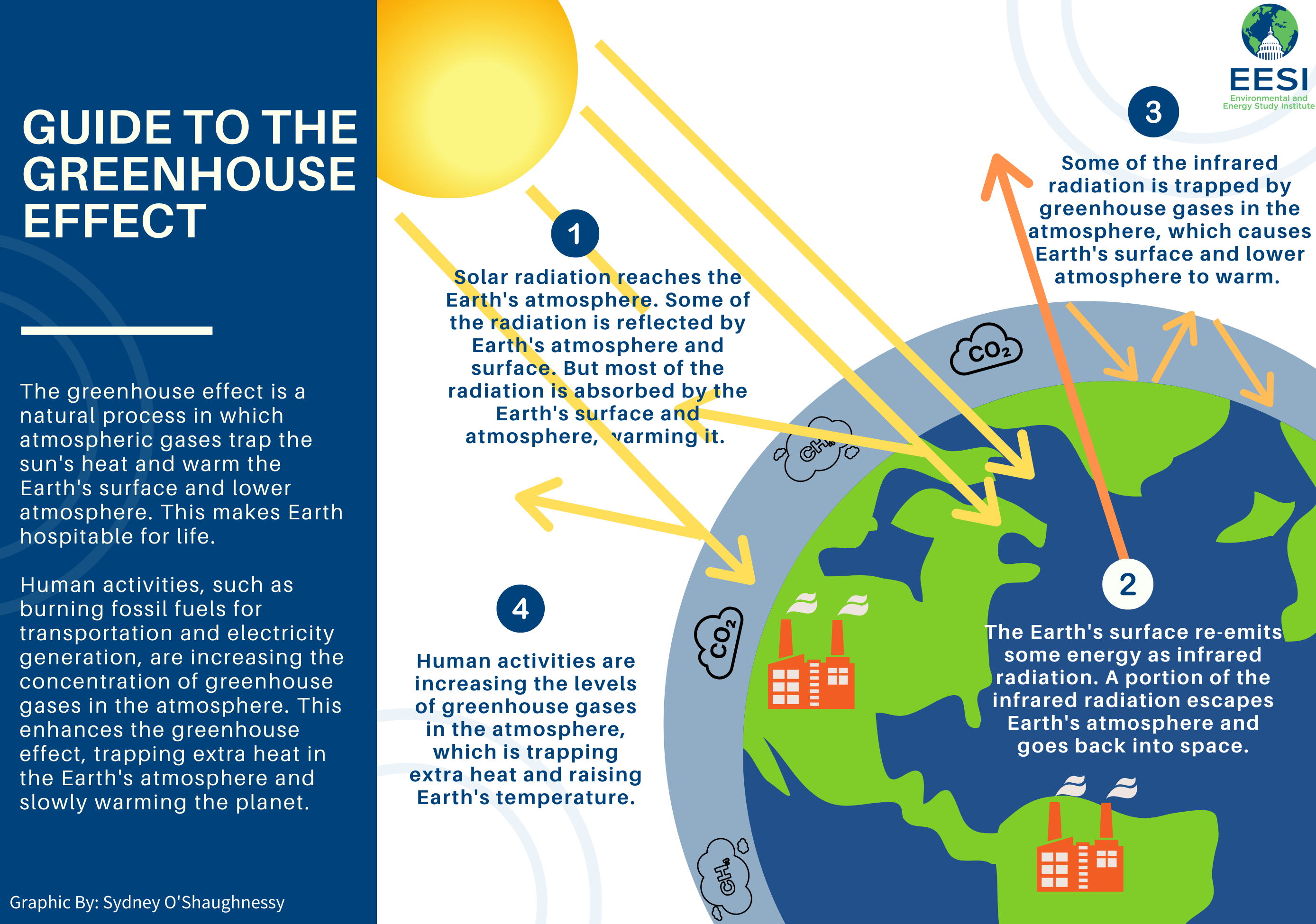



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
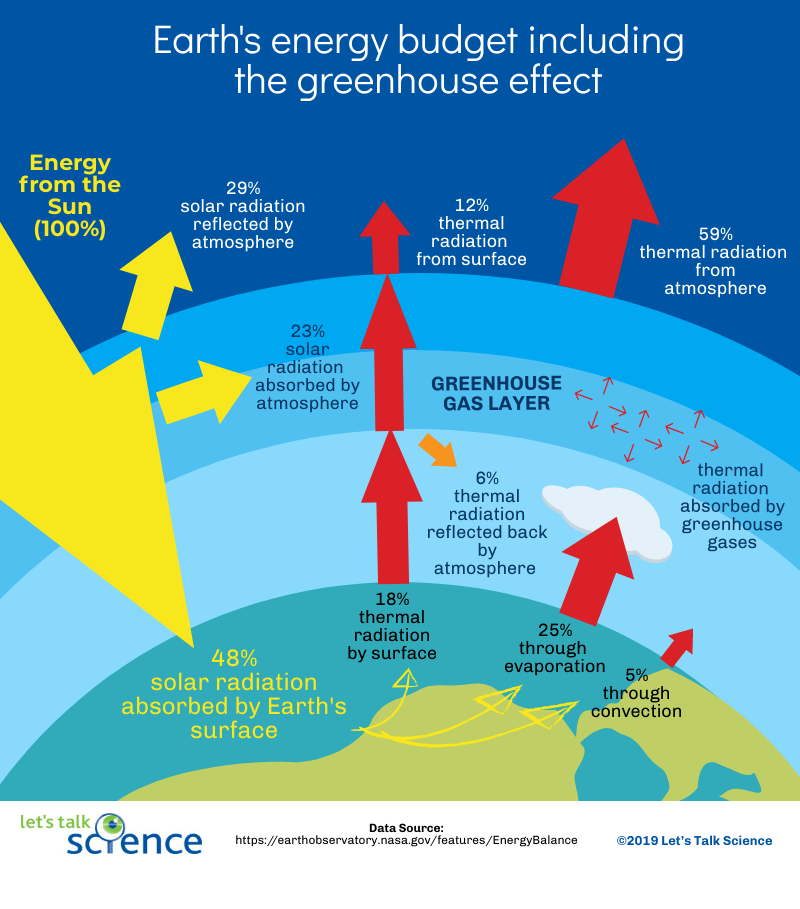



What Is Ocean Warming And Why Does It Matter Let S Talk Science




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Green House Effect



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



1
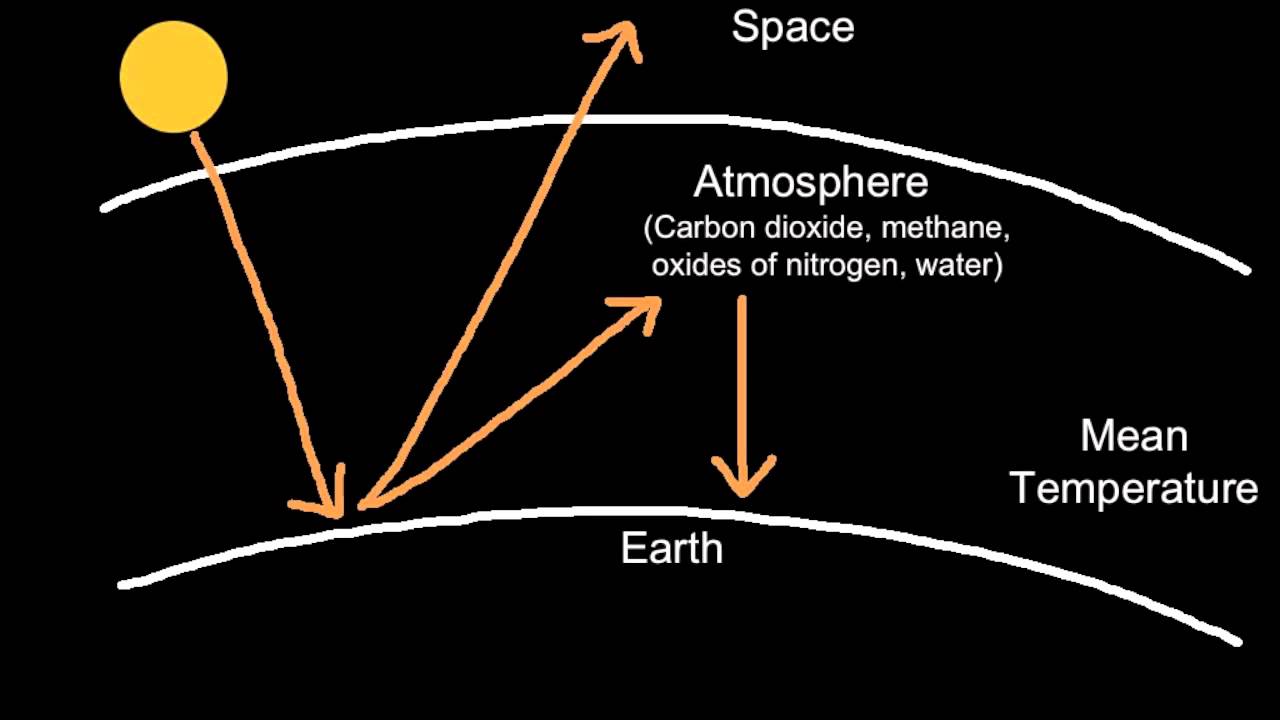



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Q8 Describe The Green House Ef Lido
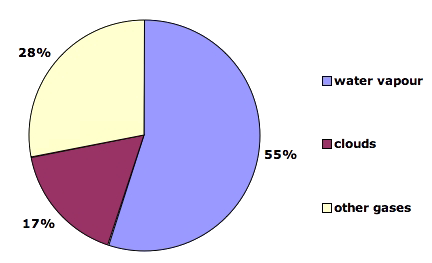



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿